Heart Failure Management
Download / Print Section as PDF

Integrated Chronic Heart Failure Management Programme (I-CHaMP)
“Heart Failure is not a single pathological diagnosis , but a clinical syndrome consisting of cardinal signs (e.g. breathlessness, ankle swelling and fatigue) that may be accompanied by signs e.g. elevated jugular venous pressure, pulmonary crackles, and peripheral oedema McDonagh et al. (2021)
It is estimated that there is a 1 in 5 lifetime risk of developing Heart Failure (HF). The prevalence of diagnosed HF is at least 1-2% of adults rising to 10% in the over 70s. The true prevalence of the condition fails to capture the full magnitude of the undiagnosed. Early diagnosis is key so that treatments can be initiated which are proven to improve quality of life, reduce hospitalisation and improve survival from this condition.
A focus on prevention strategies and risk factor management are needed to allay future prospects of an increased burden of disease given the ageing population, better cardiovascular treatments and rising risk factors of Obesity and Diabetes.
In Ireland the National Heart Clinical Program provides guidance on the management of HF in the Model of Integrated Care (MOC) for Heart Failure, 2021. The HF MOC proposes to change how we deliver care to people with HF or at risk for HF and support a national model of integrated care through partnerships between the patient, the acute services and primary care (HSE, 2021).
Aims and objectives of the Model of Integrated Care (MOC) for Heart Failure
AIM:
- To improve the quality of care for patients with or at risk of HF
- To prevent or delay the onset of HF
- To improve the delivery of care to people with HF across all five levels of care
- To improve the quality of life and prolong life for patients with HF
- To ensure care is in line with the objectives of the National Heart Programme (NHP)
OBJECTIVE:
- Every patient with symptoms of HF is diagnosed correctly without delay
- Every patient with HF is managed within a structured programme
- Implement targeted programme to prevent HF
- Reduce hospital dependency
The model of integrated care (MOC) for HF builds on the level of services proposed by the Integrated Care Programme for the Prevention and Management of Chronic Disease, (HSE, 2020). The five levels of care are outlined and demonstrate a partnership approach to care delivery between the patient, GP, community services and acute hospital services.
The five levels of care in the integrated MOC are:
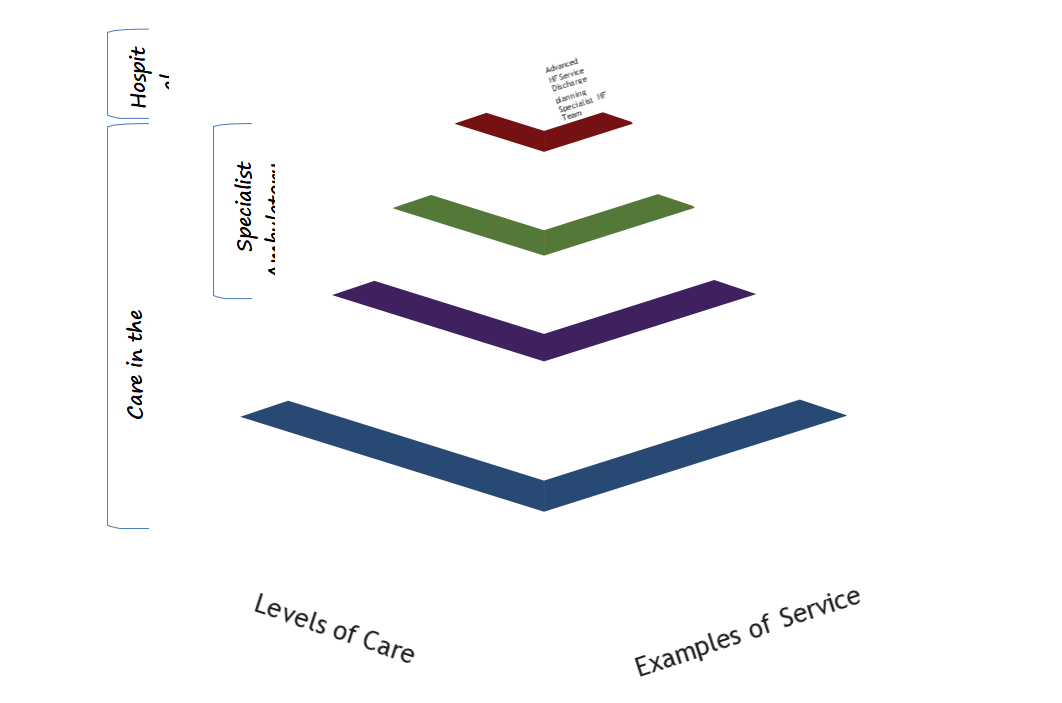
The patient can move back and forwards between the five levels as clinical need dictates, with the GP and the primary care teams having a lead role in supporting and managing patients with chronic disease and referring to a specialist when appropriate.
Level 0- Self Management Supports
- Supporting Self –care, educating patients/carers in self -care strategies
- Risk factor management primary and secondary prevention strategies- Making Every Contact Count (MECC)
- Signposting patients towards peer support-e.g. HSE Living Well programme, Croí programmes and supports, Irish Heart Foundation Heart Support network
- Signposting patients towards heart failure education resources: information books and online webinars run by Croí and the Irish Heart foundation, Heart failure matters website
Level 1 General Practice Prevention
- Targeted risk factor management for CVD prevention
- Identification and screening high risk populations- STOP HF programme
Level 2 Community Specialist Ambulatory Care
- GP access to community diagnostics
- Support management of stable HF via specialised services for general practice including:
- Advice on management of stable HF
- Virtual clinics (Consultant-GP) to give access to specialist opinion facilitating GP management/ hospital avoidance
- Hub staff GP/GPN education on managing chronic heart failure
Level 3 Acute Specialist Ambulatory Care
- Access to specialist review in ambulatory hub
- Access to advice on management of emerging HF deterioration
- Access to Rapid access diagnostic clinics
- Access to Nurse led medication optimisation clinics
- ANP/CNS led clinics to support post discharge 12 week programme.
- Access Cardiac Rehab- other MDT supports to complement holistic care
Level 4 Specialist Hospital care
- Access to urgent review ED/AMAU
- Inpatient team management of acute heart failure
- Specialist cardiology services including coronary intervention, specialist imaging, structural heart services, cardiothoracic surgery, cardioversion, pacing clinics.

What patients should I register on this programme – and when?
CDM Phasing Table

